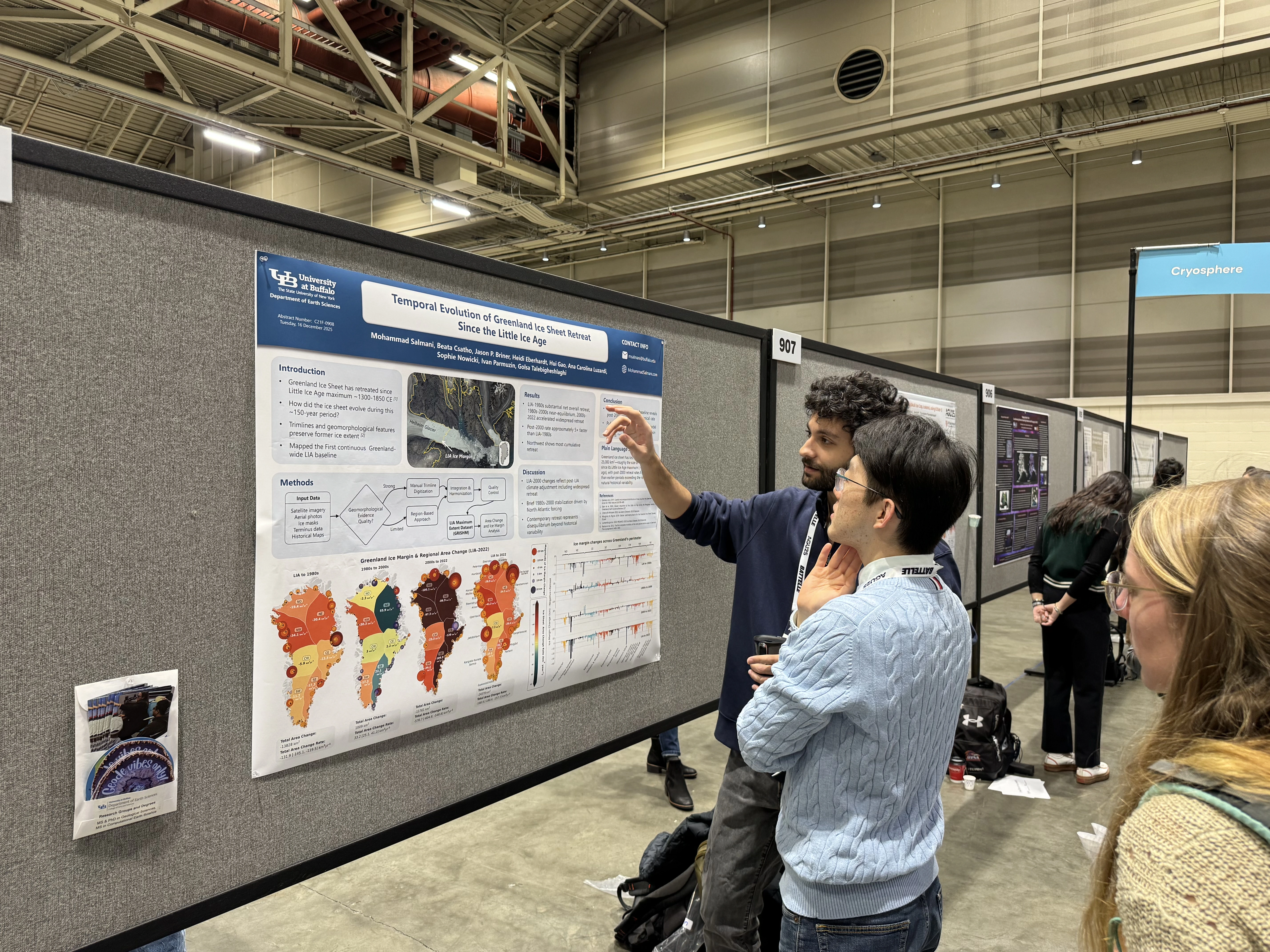
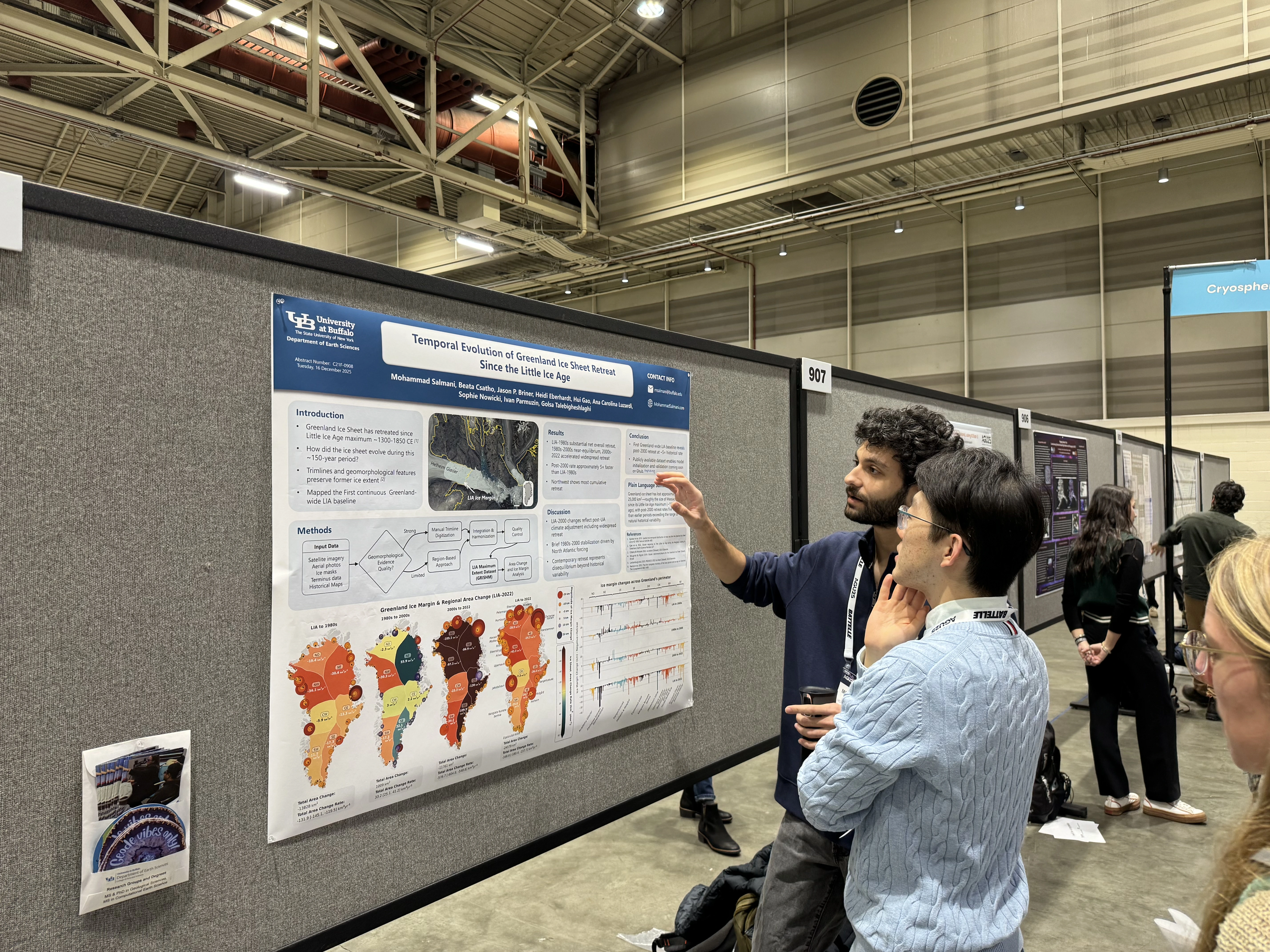
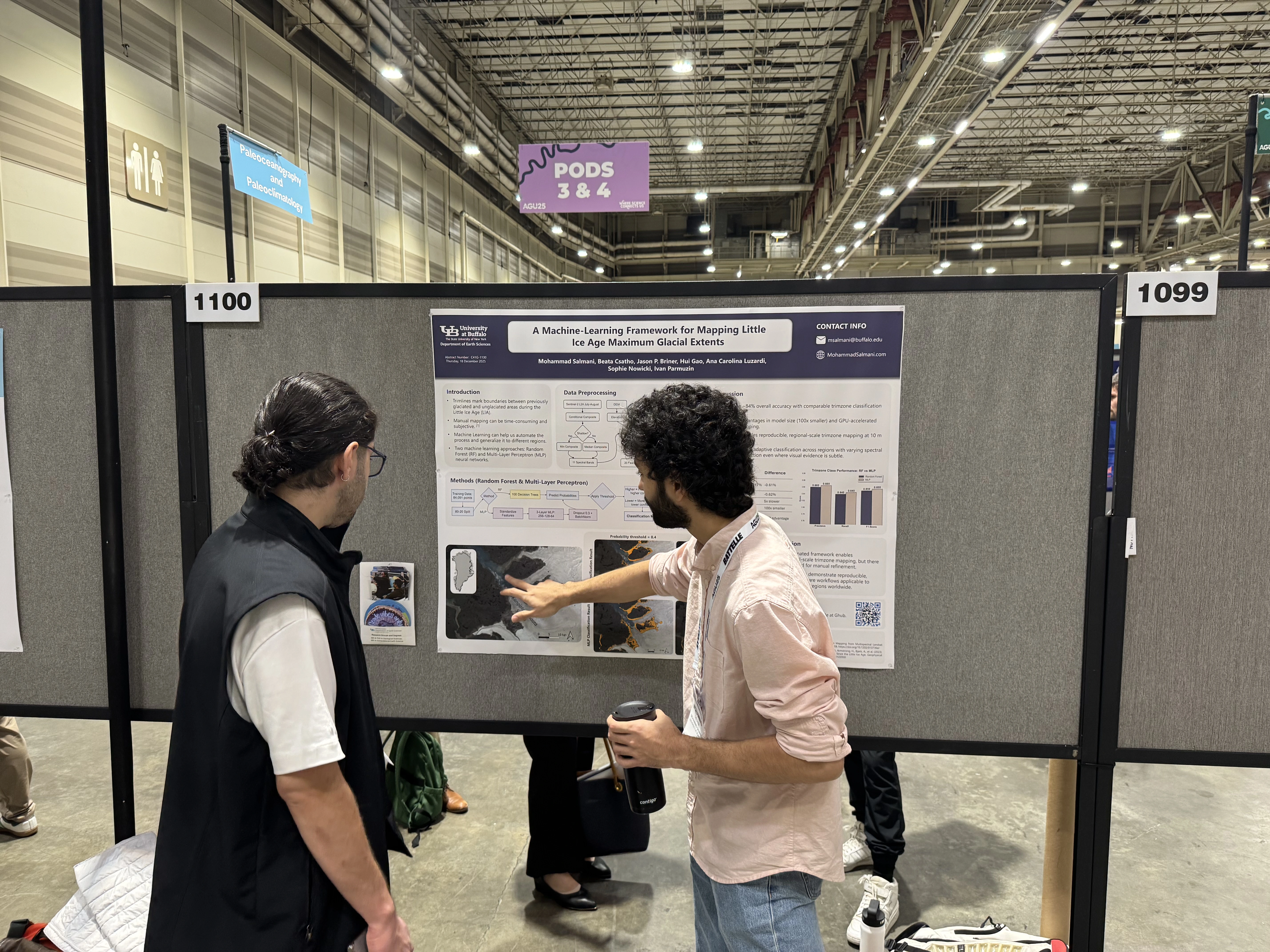
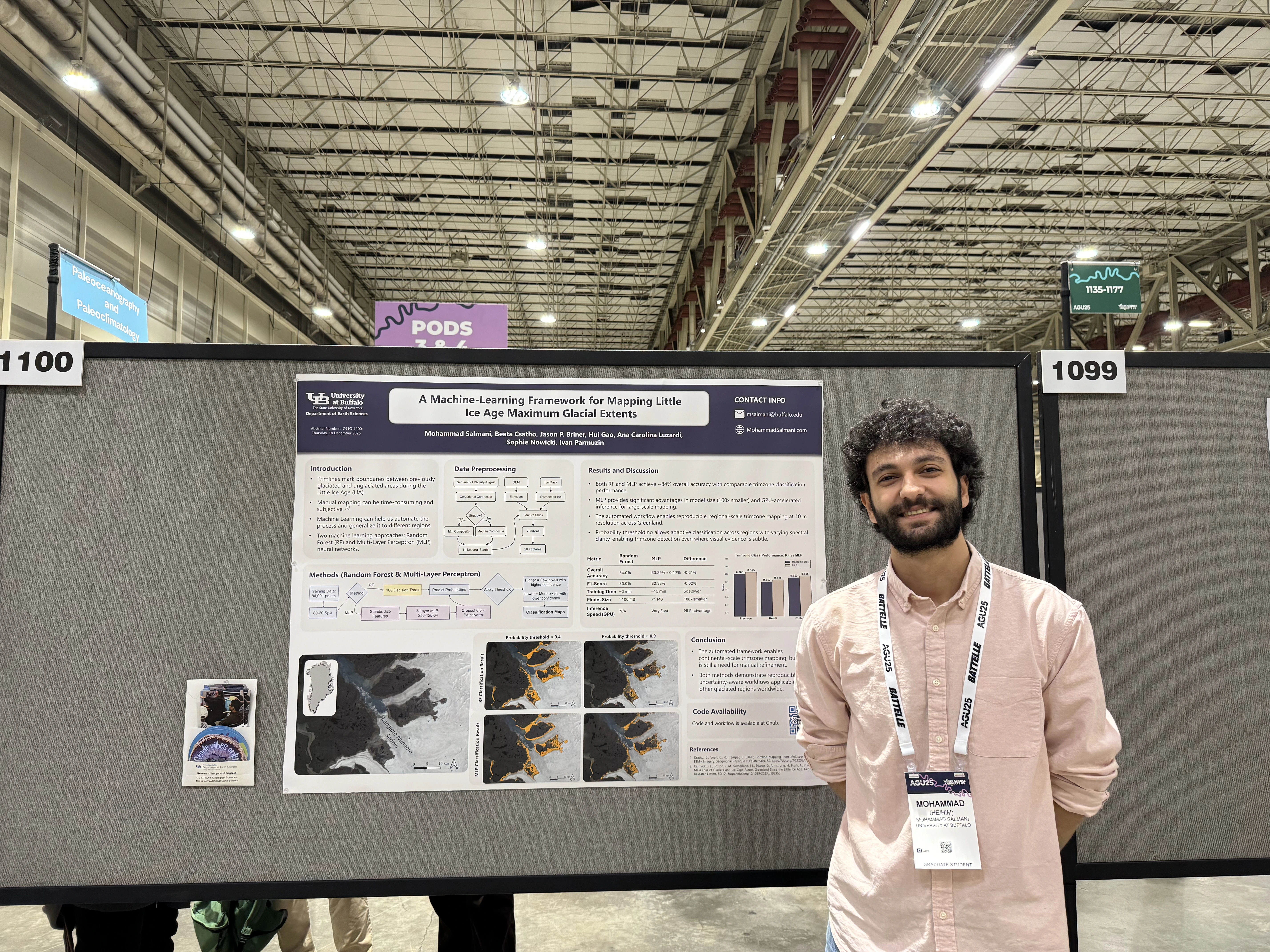
I am a PhD student and Research Assistant at the Remote Sensing Lab at the University at Buffalo, specializing in Earth Sciences and Glaciology. My research focuses on leveraging remote sensing techniques to investigate ice sheet dynamics and their implications for sea level rise and climate change.
Currently, I am engaged in a project aimed at determining the highest extent of the Greenland ice sheet using Machine Learning and classification methods. My work seeks to enhance our understanding of glacial behavior and its critical role in the Earth's climate system.